A satiating diet is a type of diet plan that focuses on foods that are high in fiber, protein, and healthy fats, and low in carbohydrates and sugar. The goal of a satiating diet is to help people feel full and satisfied after eating, which can lead to weight loss and improved overall health.
The Satiating Diet is a diet plan that emphasizes the importance of feeling full and satisfied after eating a meal. This approach to eating focuses on choosing high-protein and high-fiber foods that take longer to digest and leave you feeling full for longer periods of time. It emphasizes a balanced approach to eating that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods, such as lean meats, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, and restricts calorie-dense and processed foods. The aim of the Satiating Diet is to help people achieve a healthy weight and avoid overeating.
Satiating diet is a type of eating plan that emphasizes the importance of feeling full and satisfied after every meal. The goal of this diet is to help individuals control their food cravings and reduce overeating. Unlike other diets that focus on calorie restrictions, the satiating diet focuses on the quality and variety of foods that are consumed. The emphasis is on eating whole, unprocessed foods that are rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats, which help to keep hunger at bay. By following this diet, individuals are able to eat satisfying meals, lose weight, and maintain a healthy lifestyle.

Table of Contents
Pros of Satiating Diet
Satiating diets have become increasingly popular in recent years due to the numerous benefits they offer. A satiating diet is one that is rich in nutrient-dense, high-fiber foods that help you feel full and satisfied, reducing the urge to snack between meals. Here are some of the key benefits of a satiating diet:
- Helps control weight: Satiating diets help control weight by reducing calorie intake and reducing the urge to snack between meals. This results in a lower calorie intake and helps with weight loss.
- Reduces hunger: Foods that are high in fiber and protein help you feel full and satisfied, reducing hunger pangs and the urge to snack. This makes it easier to stick to a healthy eating plan and avoid unhealthy foods.
- Increases nutrient intake: A satiating diet is typically rich in nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods provide essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals that are crucial for good health.
- Improves digestion: Fiber-rich foods help regulate digestion, reducing the risk of digestive issues such as constipation and diarrhea. This also helps keep you feeling full
Type of Pros of Satiating Diet
- Helps Control Hunger: A satiating diet is designed to help people feel full and satisfied after eating, which can help control hunger and prevent overeating.
- Promotes Weight Loss: By filling up on foods that are high in fiber, protein, and healthy fats, and low in carbohydrates and sugar, a satiating diet can help promote weight loss by reducing the number of calories consumed.
- Improves Heart Health: By reducing the amount of unhealthy fats and carbohydrates in the diet, a satiating diet can help improve heart health by reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Boosts Energy Levels: By eating more protein, healthy fats, and fiber, a satiating diet can help boost energy levels and improve overall health.

Cons of Satiating Diet
Satiating diets can be quite restrictive, often limiting the intake of certain foods and food groups. This can lead to malnutrition and a lack of essential nutrients that the body needs to function properly. Additionally, some people may find it difficult to stick to strict guidelines and end up feeling deprived, which can lead to binge eating or other disordered eating patterns.
Another disadvantage is the cost of high-quality, whole foods that are typically recommended in satiating diets. These foods can be more expensive than processed and junk foods, making it challenging for people on a budget to follow this type of diet.
Finally, it can be challenging to find variety in a satiating diet, as the focus is on consuming low-calorie, high-fiber foods. Over time, this can get monotonous and leave people feeling unsatisfied with their food choices.
- Restrictive: A satiating diet can be restrictive, as it limits the types of foods that can be eaten.
- Difficult to Follow: Some people may find it difficult to follow a satiating diet, as it requires careful meal planning and preparation.
- Unpleasant Side Effects: Some people may experience unpleasant side effects when transitioning to a satiating diet, such as headaches, fatigue, and digestive problems.
How It Works
A satiating diet works by filling up on foods that are high in fiber, protein, and healthy fats, and low in carbohydrates and sugar. This helps to reduce the number of calories consumed while keeping the body feeling full and satisfied.
The foods that are recommended on a satiating diet include lean proteins such as chicken, fish, and turkey, as well as healthy fats such as avocado, olive oil, and nuts. In addition, a satiating diet also recommends eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which are high in fiber and nutrients.
In conclusion, a satiating diet can be a helpful way to promote weight loss and improve overall health, but it may not be suitable for everyone. It is important to speak with a healthcare provider before starting any new diet plan to determine if it is the right fit for your individual needs and health goals.
How Satiating Diet Works
The key to a successful satiating diet is to choose foods that are high in protein, fiber, and healthy fats. These nutrients have been shown to be the most effective in reducing hunger and promoting fullness.
Protein: Protein is an essential nutrient that is important for building and repairing muscle tissue. It also helps to regulate hunger and fullness by slowing the digestion of food and increasing feelings of fullness. High-protein foods include poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, beans, and nuts.
Fiber: Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that cannot be broken down by the body and passes through the digestive system largely undigested. This helps to promote feelings of fullness and reduce hunger. High-fiber foods include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts.
Healthy Fats: Healthy fats are essential for overall health and can help to regulate hunger and fullness by slowing the digestion of food and increasing feelings of fullness. Healthy fat sources include olive oil, avocados, nuts, and fatty fish.
In addition to these three key nutrients, a satiating diet should also include plenty of water, which helps to hydrate the body and promote feelings of fullness. It is also important to limit the consumption of processed foods, which are often high in added sugars and unhealthy fats, and can contribute to overeating and weight gain.
Description of the Control diet and the Satiating diet.
Control diet : A control diet is a diet that is designed to serve as a reference or baseline for comparison purposes in research studies. This diet is typically low in energy density, high in fiber, and contains a balance of macronutrients (carbohydrates, protein, and fat). The goal of a control diet is to maintain a stable body weight and to provide a standardized baseline for other diets to be compared against.
The control diet is a term used to describe a dietary regime that is maintained as a standard or reference for comparison against experimental diets. This type of diet is typically designed to provide the recommended daily allowances of all essential nutrients and is considered to be balanced and nutritionally adequate. It may also serve as a baseline for comparing the effects of different diets, such as a low-fat or low-carbohydrate diet, on weight loss, blood sugar levels, and other health outcomes. The control diet is usually composed of a mix of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, and may include a limited amount of added sugars and processed foods.
Satiating diet : A satiating diet is a diet that is designed to promote feelings of fullness and satisfaction. This type of diet typically contains foods that are high in fiber and protein, low in energy density, and slow to digest. Foods that are high in fiber and protein take longer to digest, thus keeping the person feeling full and satisfied for a longer period of time. The goal of a satiating diet is to help people eat less and avoid overeating, leading to weight loss or maintenance.
Avoid veins disease from using satiating diet
A balanced and nutritious diet can help prevent various health problems, including vein disease. Eating a diet rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals can improve circulation and reduce the risk of vein disease. Here are some suggestions for healthier eating habits:
- Increase your intake of fruits and vegetables: They are high in fiber and vitamins that can improve blood flow and reduce the risk of vein disease.
- Consume lean proteins: Foods such as chicken, fish, and legumes are a good source of lean protein that can help maintain strong and healthy veins.
- Limit processed foods: Processed foods are high in salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats, which can contribute to vein disease.
- Hydrate: Drinking plenty of water can help maintain healthy circulation and prevent vein disease.
- Avoid unhealthy fats: Foods high in unhealthy fats, such as fried foods and processed snacks, can increase the risk of vein disease.
It’s important to remember that maintaining a healthy diet is just one part of a comprehensive approach to prevent vein disease. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and not smoking are also important
Types of vein Disease
1 Chronic venous insufficiency
2 varicose vein
3 Spider vein
4 Blood clots
Chronic venous insufficiency
Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) is a medical condition in which the veins in the legs have difficulty carrying blood back to the heart, resulting in blood pooling in the lower legs. This condition is caused by a variety of factors, including aging, genetics, obesity, long periods of standing or sitting, and previous blood clots.
Symptoms of CVI include swelling in the legs, pain or aching, skin discoloration or ulcers, and a heavy or tired feeling in the legs. In severe cases, the skin may break down and lead to infections.
Diagnosis is typically made through a physical examination and imaging tests, such as ultrasound or venography. Treatment for CVI may involve lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight and elevating the legs, as well as compression stockings or other medical devices to help improve circulation. For more severe conditions, surgery may become a necessary course of action.
Early detection and proper treatment of CVI is important to prevent complications and improve quality of life.
varicose vein
Varicose veins are enlarged and distorted veins that are visible just below the skin’s surface. They usually occur in the legs and can be blue or dark purple. Varicose veins are caused by weakened valves in the veins which allow blood to flow backwards and pool in the veins. This can cause pain, aching, and swelling in the legs. In severe cases, it can also lead to skin ulcers, blood clots, and other complications. Treatments for varicose veins include lifestyle changes, compression stockings, sclerotherapy, endovenous laser treatment, and surgery.
Types of varicose vein
- Superficial varicose veins: These are the most common type of varicose veins and occur close to the surface of the skin. They are usually blue or green in color and appear twisted and swollen.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): These are blood clots that occur in the deep veins of the legs and are often a complication of varicose veins.
- Perforating veins: These veins connect the deep and superficial veins and can become damaged as a result of varicose veins.
- Reticular veins: These are small, blue or green veins that are often found just below the surface of the skin. They are often a precursor to the development of varicose veins.
- Saphenous veins: These are the largest veins in the legs and are often affected by varicose veins. They can be found in the inner thigh and can also be a source of DVT.
- Venous ulcers: These are open sores that occur as a result of poor circulation in the legs and can be a complication of varicose veins.

VARICOSE VEINS TREATMENT
Varicose veins are a common condition that affects millions of people around the world. They are swollen, twisted veins that are often visible just under the skin. Varicose veins can cause discomfort, pain, and even serious health problems if left untreated. However, there are many effective treatments available that can help relieve the symptoms and improve the appearance of varicose veins.
Compression Stockings: One of the most effective treatments for varicose veins is wearing compression stockings. These special stockings help to improve blood flow and reduce swelling in the affected veins. They work by applying gentle pressure to the legs, which helps to keep blood from flowing backwards and pooling in the veins.
Lifestyle Changes: Making simple lifestyle changes can also help to reduce the symptoms of varicose veins. This includes regular exercise, eating a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding long periods of standing or sitting.
Sclerotherapy: Sclerotherapy is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a special solution to close off the affected veins. The solution is injected into the vein, causing it to shrink and eventually disappear. This procedure is highly effective and has minimal side effects.
Laser Therapy: Laser therapy is another effective treatment for varicose veins. The laser is used to heat and destroy the affected veins, causing them to shrink and disappear. This procedure is minimally invasive and has minimal side effects.
Radiofrequency Ablation: Radiofrequency ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that uses radio waves to destroy the affected veins. The radio waves heat the veins, causing them to shrink and disappear. This procedure is highly effective and has minimal side effects.
Surgery: In severe cases of varicose veins, surgery may be necessary to remove the affected veins. This procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia and involves making small incisions in the legs to remove the veins.
Treatment for varicose veins can include:
- Compression stockings: Wearing compression stockings can help improve blood flow and reduce swelling in the legs.
- Lifestyle changes: Simple changes such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding standing or sitting for long periods can help reduce the symptoms of varicose veins.
- Endovenous laser treatment (EVLT): In this minimally invasive procedure, a laser fiber is inserted into the affected vein and used to heat and seal the vein shut.
- Sclerotherapy: This is a procedure in which a solution is injected into the affected vein, causing it to shrink and disappear over time.
- Radiofrequency closure: This is a minimally invasive procedure that uses radiofrequency energy to heat and shrink the affected vein.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical removal of the affected vein may be necessary.
It is important to consult with a doctor to determine the best treatment option for your specific case
3. Spider vein
Spider veins are small, red, blue, or purple veins that often look like spider webs or branches on the skin’s surface. They usually occur on the legs and face and are caused by a variety of factors, including age, genetics, pregnancy, and standing or sitting for long periods of time. They are usually not a serious health concern but can be cosmetically unappealing and cause discomfort or itching. Treatment options for spider veins include sclerotherapy, laser therapy, or the use of compression stockings.
Types of Spider veins
- Reticular veins: They are small, blue or green veins that are usually less than 1 millimeter in diameter.
- Telangiectasias: They are tiny, red veins that are usually less than 2 millimeters in diameter.
- Spider angiomas: They are small, red veins that resemble a spider’s web and are often found on the face or neck.
- Venous lake: They are dark blue or purple veins that are often found on the lips or face.
- Cherry angiomas: They are small, red or purple bumps that are often found on the trunk or arms.
- Venous malformations: They are clusters of veins that are larger and more complex than other types of spider veins.
- Capillary malformations: They are clusters of small, red or purple veins that are often found on the face or legs
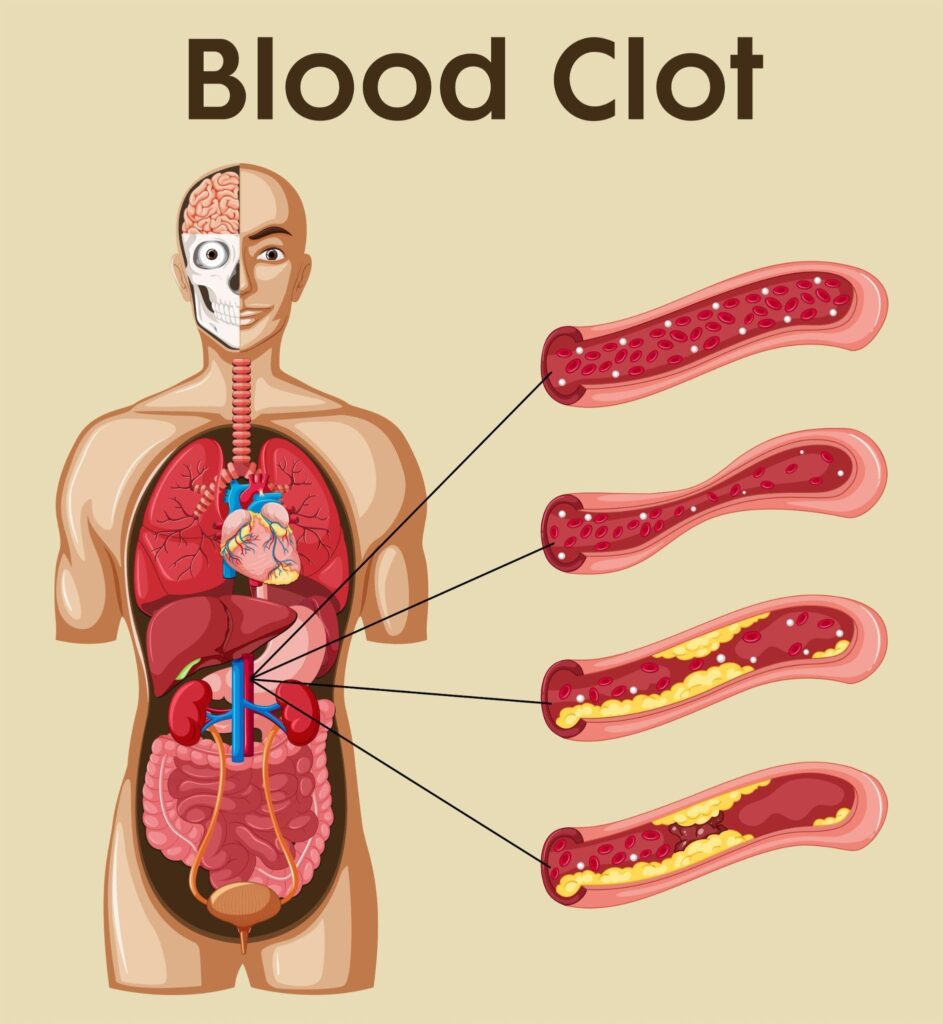
4. Blood clots
Are a mass of clumped blood cells that can form in the veins or arteries. Blood clots can be dangerous because they can obstruct the flow of blood, leading to serious health problems such as stroke, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), or pulmonary embolism. Risk factors for blood clots include immobility, certain medical conditions, surgery, pregnancy, and certain medications. Symptoms of blood clots may include pain or swelling in the affected limb, redness or warmth, and changes in skin color. Treatment options include anticoagulant medications, mechanical devices to remove clots, and surgery.
Blood clots are dangerous as they can lead to life-threatening conditions like stroke or heart attack. A blood clot can form anywhere in the body and can be caused by various factors such as prolonged bed rest, surgery, or injury. Here are some tips to help you avoid blood clots:
- Stay Active: Regular exercise helps to improve circulation and prevent blood clots from forming. Try to do some physical activity for at least 30 minutes a day.
- Stop Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of blood clots and heart disease. If you smoke, it is essential to quit to lower your risk of developing blood clots.
- Wear Loose Clothing: Tight clothing can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of blood clots. Wearing loose-fitting clothing, especially during long periods of travel, can help to reduce the risk.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of blood clots. Maintaining a healthy weight through proper diet and exercise can lower the risk of blood clots.
Conclusion :
The Satiating Diet is a healthy and balanced approach to eating that emphasizes the consumption of satiating foods, which are those that help you feel full and satisfied. This diet encourages the consumption of whole, unprocessed foods such as lean proteins, healthy fats, and fiber-rich carbohydrates, while limiting the intake of empty calorie foods that provide little nutrition. The Satiating Diet promotes a healthy relationship with food and helps prevent overeating, while still allowing for flexibility and moderation. It is a great option for anyone looking to achieve weight loss, maintain a healthy weight, or simply improve their overall health.
FAQs
What is the Satiating Diet?
The Satiating Diet is a dietary approach that focuses on eating foods that are high in fiber, protein, and healthy fats to promote feelings of fullness and satisfaction, leading to decreased calorie intake and weight loss.
What kind of foods are included in the Satiating Diet?
The Satiating Diet includes foods such as whole grains, lean protein sources, low-fat dairy products, vegetables, and healthy fats like olive oil, nuts, and avocado. Processed and high-calorie foods are avoided.
Is the Satiating Diet scientifically proven?
Studies have shown that high-protein, high-fiber diets can be effective in reducing calorie intake and promoting weight loss. However, more research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of the Satiating Diet.
Is the Satiating Diet safe for everyone to follow?
As with any diet, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider before making any changes to your eating habits. The Satiating Diet may not be suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as digestive disorders or food allergies.
Can the Satiating Diet be combined with other weight loss strategies?
Yes, the Satiating Diet can be combined with other weight loss strategies, such as exercise and stress management, for a more comprehensive approach to health and wellness. It is important to consult a healthcare provider before making any significant changes to your diet or lifestyle.

