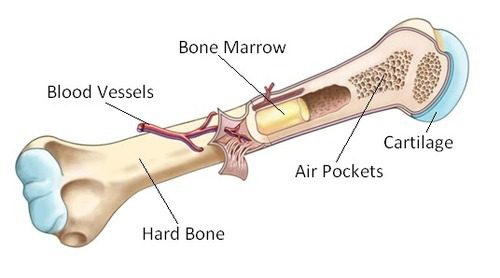
Bone marrow transplant is described as a tissue comprising the centre of large bones and which contains two types of stem cells hemopoietic and stromal. It is mainly found in medullary cavities, i.e. at the centres of bones and is where circulating blood cells are produced, and this the process is known as hematopoiesis. Bone marrow undergoing hematopoiesis is red in colour because of the presence of red blood cells and bone marrow not undergoing hematopoiesis is yellow in colour. Bone marrow is a fatty spongy tissue which is located inside your bones, and that creates below-listed parts of blood:
- Red blood cells that carry out oxygen and nutrients throughout the body
- White blood cells those are liable for fighting infection
- Platelets which are responsible for the formation of clots
Bone marrow transplant
Bone marrow is the procedure done to replace bone marrow that has been damaged or else destroyed by any kind of infection, disease or chemotherapy. This entire process involves transplanting blood stem cells in the patient’s body. These blood stem cells travel to the bone marrow where they produce new blood cells and also promote the growth of new marrow. Bone marrow transplant will replace your damaged stem
cells with healthy cells and which will help your body to make enough white
blood cells, red blood cells to avoid bleeding disorders, anaemia, and infections.
Why you need a bone marrow transplant?
A bone marrow transplant is recommended by a doctor when a patient’s marrow is not healthy enough to function properly.
Some causes of this condition can be chronic infections, disease or else
cancer treatments. The main goal of bone marrow transplant is to cure numerous diseases along with types of cancers. Below we have listed some reasons why there is a need for bone marrow transplant:
- Cancers that affect marrow like lymphoma, leukemia, as well as multiple myeloma
- Damaged bone marrow because of chemotherapy
- Congenital neutropenia which is a disorder that causes recurring infections
- Because of thalassemia, that is an inherited blood disorder in which the body makes an abnormal form of hemoglobin
- Sickle cell anemia which is a blood disorder that causes misshapen red blood cells
- Aplastic anemia, because of which the marrow stops making new blood cells
Types of bone marrow transplants
There are different types of bone marrow transplants and which entirely depends upon who the donor is. It includes:
- Autologous bone marrow transplant:
In this type of transplant, the patient has donated stem cells of its own to be used for their own transplant.
- Allogeneic bone marrow transplant:
This donor will be selected as per their HLA type, i.e. genetic match.
- Siblings (Matched related donor)
In this, brothers and sisters are the primary chooses as donors as their HLA matches automatically.
- Parent/Children (Haploidentical stem cell transplant):
It is when the donor is a parent, and the genetic match is at least half with the patient
- Unrelated bone marrow transplants, i.e. UBMT or else matched unrelated donor, i.e. MUD:
In this case, the HLA matched stem cells are taken from an unmatched donor
- Umbilical cord blood transplant:
In this case, stem cells are taken instantly through the umbilical cord after the delivery of an infant. These stem cells are tested, counted, typed and frozen till the time they are required.
Bone marrow transplant hospitals in India
- Indraprastha Apollo Hospital, New Delhi
- Medanta – The Medicity, Gurgaon
- Kokilaben Dhirubhai Ambani Hospital, Mumbai
- Apollo Hospitals, Greams Road, Chennai
- Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurgaon
- BLK Super Specialty Hospital, New Delhi
The success rate of bone marrow
transplant is high; however, it totally depends on how closely the donor and
The recipient genetically matches each other. In some case, it is difficult to
find a good match among unrelated donors. The recovery time after a bone marrow transplant is about three months. In some cases, it may take up to a year to recover.
Corneal Transplantation in India